10 th form 07.02.2022
Неопределенные местоимения some, any, no и правила их употребления
В английском языке some, any и no относятся к категории неопределенных местоимений. Ниже будут рассмотрены правила употребления some, any и no, а также их производных.
Правила употребления some
1. Использование some с неисчисляемыми существительными в значении «немного»:
There is some tea in the cup. – В чашке есть немного чая.
К неисчисляемым существительным английского языка, как правило, относятся такие категории существительных, как вещественные, абстрактные, то есть то, что нельзя посчитать.
2. Также some употребляется с исчисляемыми существительными, стоящими во множественном числе в значении «несколько», «некоторые»:
Some pupils brought interesting books. – Несколько учеников/ некоторые ученики принесли интересные книги.
3.Еще один случай употребления неопределенного местоимения some – с исчисляемыми существительными в единственном числе, при этом значение будет «какой-то»: Some guy called and wanted to talk with you. – Звонил какой-то парень и хотел поговорить с тобой.
Как правило, some и его производные употребляются в утвердительных предложениях, но также есть случаи, когда местоимение some используется в вопросительных предложениях.
1. Когда мы хотим попросить о чем-то или наоборот, предложить что-то:
Would you like some soup? – Не хотели бы Вы немного супа?
Can I have some cold milk, please? – Можно мне холодного молока, пожалуйста?
2. Когда мы задаем вопрос, ответ на который предполагается быть утвердительным:
What a smell! Are you cooking something tasty? – Какой запах! Ты готовишь что-то вкусненькое?
Есть еще одно правило употребления some в английском языке. Местоимение some можно использовать с предлогом of в значении «некоторые из». В данном случае перед существительным необходимо поставить либо определенный артикль, либо указательное или притяжательное местоимение.
Some of my friends are going to Moscow this week. – Некоторые из моих друзей собираются в Москву на этой неделе.
Some of the houses were destroyed during the fire. – Некоторые из домов были разрушены во время пожара.
Правило употребления местоимения any
Местоимение any и все его производные обычно употребляются в отрицательных и вопросительных предложениях:
I don’t have any problems at school. –У меня нет проблем в школе.
Do you have any news? – Есть какие-нибудь новости?
Также есть правила для случаев, когда any употребляется в утвердительных предложениях:
1. Когда имеется в виду «любой», «всякий», «что угодно», «где угодно», «как угодно»: Anyone can do this. – Любой может это сделать.
2. В придаточных предложениях после «if»: If you have any questions let me know. – Если у вас будут вопросы, дайте знать.
3. Если в предложении уже имеются нижеперечисленные наречия и предлог с отрицательным значением:
- Hardly
- Scarcely
- Never
- Without
- Seldom
- Rarely
I seldom go anywhere at night. – Я очень редко выхожу куда-либо ночью.
Without any doubt, he is a good person. – Без сомнения, он хороший человек.
He never stays alone at home. – Он никогда не остается дома один.
Если местоимение any употребляется с предлогом of, то на русский язык конструкция будет переводиться как «любой»:
You can take any of these books they are all very interesting. – Можешь взять любую из этих книг, они все очень интересные.
Но стоит запомнить правило с any, что производные от местоимения, такие как anyone, anybody, anywhere, не могут использоваться с предлогом of.
После производных местоимений можно использовать наречие else в значении «еще», «кроме».
Are you going to tell me anything else? – Ты хочешь мне сказать что-то еще?
Does anybody need extra paper? – Кому-нибудь еще нужна бумага?
Правило употребления some, any и артиклей a/an
Есть случаи, когда можно задуматься над выбором между some, неопределенным артиклем «а» и нулевым артиклем. Этот случай касается неисчисляемых существительных.
- Could you give me some water, please?
- Could you give me a water, please?
- Could you give me water, please?
Все три предложения переводятся как «Не могли бы вы дать мне воды, пожалуйста?». Разница состоит в том, что в первом предложении мы как бы просим небольшое количество жидкости, во втором, употребляя артикль «а», мы имеем в виду, что нам нужен один стакан или чашка воды, грубо говоря, одна «порция», а в третьем варианте мы имеем в виду, что нам важна вода, а не что-то другое, неважно в каком количестве.
Правило употребления местоимения no
Местоимение no употребляется как перед исчисляемыми существительными, так и перед неисчисляемыми. Само предложение, в котором есть местоимение no приобретает отрицательное значение. Стоит отметить, что глагол в предложении с no будет всегда в положительной форме, поскольку двойного отрицания в английском языке нет.
I have no tasks to do now. – Сейчас мне нечего делать.
We have no juice at home. Please, go to the shop. – У нас дома нет сока. Пожалуйста, сходи в магазин.
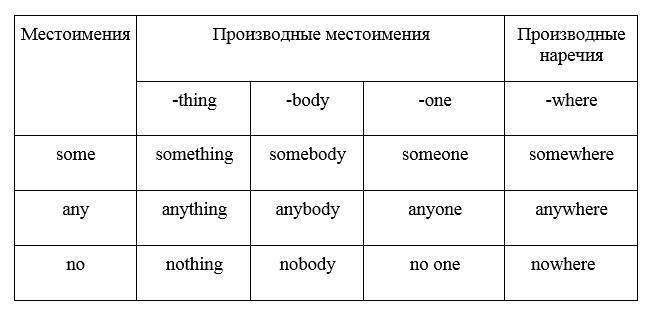
Правила образования производных местоимений и наречий от some, any, no
I have something to tell you. – Я хочу тебе кое-что сказать.
Did he see anything terrible there? – Он увидел там что-то ужасное?
I know nothing about him. – Я не знаю о нем ничего.
Somebody/ someone has stolen my purse! – Кто-то украл мой кошелек!
Has anybody/ anyone heard something about Jack? – Кто-нибудь слышал что-нибудь о Джеке?
The keys should be somewhere on the table. – Ключи должны быть где-то на столе?
We can go anywhere this summer. – Мы можем поехать летом куда угодно.
He is nowhere to be found. – Его нигде нет.
Производные местоимения, образованные от some, any, no, используются в предложении без существительных, и могут выполнять в предложении роль подлежащего или дополнения. При этом такие подлежащие согласуются со сказуемым в третьем лице единственного числа:
Nobody knows where to go. - Никто не знает, куда идти.
Something is bothering you. - Что-то тебя беспокоит.
Somebody has been sleeping in my bed. - Кто-то спал в моей кровати.
Вставьте местоимения some, any ,no, somebody, anybody, nobody, something, anything, nothing по смыслу.
1. I have ______ to tell you.
2. He never puts ______ sugar in his tea.
3. I must find______ for you to play badminton with.
4. There’s______ in my soup. It’s a mosquito.
5. Let’s have______ to drink. How about juice?
6. No, thanks. I’m not thirsty. I don’t want ______.
7. There’s______ at the door. I heard the doorbell ring.
8. Remember not to tell______ about him. It’s a secret.
9. Isn’t there______ more interesting to look at?
10. I’m thirsty. Can I have______ cold water? (просьба!)
11. I opened the door, but I could see______.
12. Susan seldom says______.
13. Stop sitting there doing______ and help me.
14. ______ can speak all the languages in the world.
15. We didn’t have______ milk for our kitten so I went out to buy it.
Вставьте some, any, no или something (anything, nothing) или somebody (anybody/ nobody) или somewhere (anywhere/ nowhere) или everybody (everything/ everywhere).
- He has got _________ money. He can’t spend his holidays abroad any more.
- The student didn’t understand ________, because he heard_______
- I need to buy a lot of things. There isn’t _______ time to waste.
- Is there _______in the office?
- There is ______white in the box. What is it?
- Would you like ________juice?
- Life is not easy. ________has problems.
- I understand _______now. Thank you for your explanation.
- Do you live … near Hyde Park?
- ____came and he felt lonely.
2. He never puts ______ sugar in his tea.
3. I must find______ for you to play badminton with.
4. There’s______ in my soup. It’s a mosquito.
5. Let’s have______ to drink. How about juice?
6. No, thanks. I’m not thirsty. I don’t want ______.
7. There’s______ at the door. I heard the doorbell ring.
8. Remember not to tell______ about him. It’s a secret.
9. Isn’t there______ more interesting to look at?
10. I’m thirsty. Can I have______ cold water? (просьба!)
11. I opened the door, but I could see______.
12. Susan seldom says______.
13. Stop sitting there doing______ and help me.
14. ______ can speak all the languages in the world.
15. We didn’t have______ milk for our kitten so I went out to buy it.
Send the answers on my email el.romanova2020@mail.ru
လလလလလလလလလလလလလလ
10 th form 04.02.2022
апомните, что CAN’T и MUSTN’T часто переводятся НЕЛЬЗЯ.Запомните, чтоCAN’T — НЕЛЬЗЯ (общее правило, запрет)
MUSTN’T — НЕЛЬЗЯ (личное решение говорящего)
Упражнение 1. Выберите модальный глагол, исходя из его значения и контекста. Переведите предложения.
Когда кажется, что подходят оба глагола, выбирайте более типичную ситуацию.- You (must, can) go to bed now.
- She (may, should) read this book.
- I (must, may) go home.
- He (can, may) speak English.
- The students (must, may) use a calculator at the Maths lessons.
- My mother (can, should) cook many delicious dishes.
- My father (must, can) drive a car.
- Jack (can, must) play the guitar very well.
- You (should, must) ask his advice.
- Kate (may, can) remember a lot of words.
Упражнение 2. Составьте вопросы из слов и дайте на них краткий или полный ответ.
- your brother/ play/ table tennis/ can? – Yes, he…
- your cousin/ can/ ride a horse? – No, he…
- may/ go to/ I / the cinema? – Yes, you…
- late/ may/ come home/ she? – No, she…
- learn this poem/ must/ she/ by heart? – Yes, she…
- books/ how many/ they/ must/read? – Only two.
- wear/ smart clothes/ for the party/ should/ they? – Yes,…
- salt/ how much/ should/ put in the dish/ I ? – Just a little.
- students/ mobile/ phones/ use/ can/ at the exams? – No, they…
- children/ come to school / in time/ must? – Yes, they…
Упражнение 3. Найдите ошибки.
- You don’t can go to the party.
- He musts take his dog for a walk.
- I can to help you.
- He not must be late.
- Can his brother speaks French?
- Paul must to go there.
- You don’t must smoke here.
CAN’T — НЕЛЬЗЯ (общее правило, запрет)
MUSTN’T — НЕЛЬЗЯ (личное решение говорящего)
Упражнение 2. Составьте вопросы из слов и дайте на них краткий или полный ответ.
- your brother/ play/ table tennis/ can? – Yes, he…
- your cousin/ can/ ride a horse? – No, he…
- may/ go to/ I / the cinema? – Yes, you…
- late/ may/ come home/ she? – No, she…
- learn this poem/ must/ she/ by heart? – Yes, she…
- books/ how many/ they/ must/read? – Only two.
- wear/ smart clothes/ for the party/ should/ they? – Yes,…
- salt/ how much/ should/ put in the dish/ I ? – Just a little.
- students/ mobile/ phones/ use/ can/ at the exams? – No, they…
- children/ come to school / in time/ must? – Yes, they…
Упражнение 3. Найдите ошибки.
- You don’t can go to the party.
- He musts take his dog for a walk.
- I can to help you.
- He not must be late.
- Can his brother speaks French?
- Paul must to go there.
- You don’t must smoke here.
Send the answers on my email el.romanova2020@mail.ru
လလလလလလလလလလလလလလ
10 th form 31.01.2022
Modals – deductions about the present
Grammar explanation
We can use modal verbs for deduction – guessing if something is true using the available information. The modal verb we choose shows how certain we are about the possibility. This page focuses on making deductions about the present or future.
must
We use must when we feel sure that something is true or it's the only realistic possibility.
This must be her house. I can see her car in the garage.
He must live near here because he always walks to work.
Come inside and get warm. You must be freezing out there!
This must be her house. I can see her car in the garage.
He must live near here because he always walks to work.
Come inside and get warm. You must be freezing out there!
might, may, could
We use might, may or could to say that we think something is possible but we're not sure.
She's not here yet. She might be stuck in traffic.
He's not answering. He could be in class.
We regret to inform you that some services may be delayed due to the bad weather.
They all have the same meaning, but may is more formal than might and could.
She's not here yet. She might be stuck in traffic.
He's not answering. He could be in class.
We regret to inform you that some services may be delayed due to the bad weather.
can't
We use can't when we feel sure that something is not possible.
It can't be far now. We've been driving for hours.
She can't know about the complaint. She's promoted him to team leader.
It can't be easy for him, looking after three kids on his own.
Note that these verbs, like all modal verbs, are followed by an infinitive without to.
It can't be far now. We've been driving for hours.
She can't know about the complaint. She's promoted him to team leader.
It can't be easy for him, looking after three kids on his own.
2. Check your grammar: gap fill
Write a modal verb to fill the gaps.
1. She's won prizes for her research. She _______________ be really intelligent. 2. I'd take an umbrella if I were you. It looks like it _______________ rain. 3. It _______________ be him. He's on holiday until next week. 4. Hey guess what?! I _______________ be getting a car for my birthday! It's not completely definite yet though. 5. I can't believe you've been waiting all this time! You _______________ be really bored. 6. His car's not here. He _______________ have gone out. 7. Look how much sugar and salt it's got in it! It _______________ be good for you. 8. Have you looked next to your computer? I think you _______________ have left your keys there.
လလလလလလလလလလလလလလ
10 th form 10.11.2021
10 th form 09.11.2021
1 In what situations do we usually use PPC Tense?2 What is it`s structure?3 How do we form questions, negative sentences and short answers?4 What are the most common mistakes in using this tense?5 Write your own examples. (5)
SB p 175-176 learn grammar ruleSB p 47 ex A,B,CSB p 46 give a 2-minute talk on crimes (follow the plan in your SB p 46)
လလလလလလလလလလလလလလ
10 th form 08.11.2021
2
fingerptint /ˈfɪŋɡə(r)ˌprɪnt/
All complaints from our customers are investigated quickly and efficiently.
accuse /əˈkjuːz/
Many modern biographies falsely accuse Kipling of racism.
The prime minister publicly accused the organization of inciting unrest.
own up to
to admit that you have done something bad or embarrassing
arson
/ˈɑː(r)s(ə)n/Burglaries are on the increase in the area.
Verbs frequently used with burglary
commit a burglary: carry out, commitMost burglaries are carried out by opportunist thieves.try to stop burglaries: combat, prevent, reduceOur efforts have paid off in reducing burglary.when police deal with a burglary: investigate, record, solvePolice are also investigating burglaries at two primary schools.when someone is stolen from: experience, sufferHe’d suffered an attempted burglary.
Verbs that frequently follow burglary
happen, occur, take place80 per cent of burglaries occur when the house is empty.The burglary took place between 5.40am and 5.43am.
kidnapping /ˈkɪdnæpɪŋ/the act of kidnapping someone
the kidnap of a local businessman
murder
/ˈmɜː(r)də(r)/a murder investigation/charge/conviction
robbery
/ˈrɒbəri/a bank robbery
He was arrested and charged with armed robbery (=robbery using a gun).
shoplifting
/ˈʃɒpˌlɪftɪŋ/They have repeatedly broken the law and got away with it.
to get off
to not be punished severely or at all for something that you have been accused of in court
He was charged with manslaughter, but got off.
to lock up
same as lock away
to make off
to leave quickly, especially after doing something wrong
to run off with
to steal something or to take it without permission
A man in the street approached her and ran off with her bag.
SB p 46 ex A,B,C
SB p 45 ex D,E
Send the answers on my email el.romanova2020@mail.ru
လလလလလလလလလလလလလလ
10 th form 27.09.2021
Grammar explanation
Stative verbs describe a state rather than an action. They aren't usually used in the present continuous form.
I don't know the answer.
I'm not knowing the answer.
She really likes you.She's really liking you.
He seems happy at the moment.He's seeming happy at the moment.
Stative verbs often relate to:
- thoughts and opinions: agree, believe, doubt, guess, imagine, know, mean, recognise, remember, suspect, think, understand
- feelings and emotions: dislike, hate, like, love, prefer, want, wish
- senses and perceptions: appear, be, feel, hear, look, see, seem, smell, taste
- possession and measurement: belong, have, measure, own, possess, weigh.
Verbs that are sometimes stative
A number of verbs can refer to states or actions, depending on the context.
I think it's a good idea.
Wait a moment! I'm thinking.
The first sentence expresses an opinion. It is a mental state, so we use present simple. In the second example the speaker is actively processing thoughts about something. It is an action in progress, so we use present continuous.
Some other examples are:
have
I have an old car. (state – possession)
I'm having a quick break. (action – having a break is an activity)
see
Do you see any problems with that? (state – opinion)
We're seeing Tadanari tomorrow afternoon. (action – we're meeting him)
be
He's so interesting! (state – his permanent quality)
He's being very unhelpful. (action – he is temporarily behaving this way)
taste
This coffee tastes delicious. (state – our perception of the coffee)
Look! The chef is tasting the soup. (action – tasting the soup is an activity)
Other verbs like this include: agree, appear, doubt, feel, guess, hear, imagine, look, measure, remember, smell, weigh, wish.
Do this exercise to test your grammar again.
10 th form 24.09.2021
Test your understanding of the English lesson by answering these questions:
1. How many conditional tenses are there in English grammar?- A one
- B two
- C three
- D four
2. Which of the following is an example of the zero conditional?- A If I went out in rainy weather without an umbrella, I would get wet.
- B I will take my umbrella with me today, because it might rain.
- C If you remembered to take your umbrella with you, you wouldn't get wet.
- D If she had taken her umbrella with her, she wouldn't have got wet.
- E If you go out in rainy weather without an umbrella, you get wet.
3. Which of the following is an example of the first conditional?- A Where would you like to go on holiday if you had plenty of money?
- B If I have enough money, I will go to the south of France for a long holiday.
- C The south of France is an expensive place to go for a holiday.
- D If I had enough money, I would go to the south of France for a long holiday.
- E She would have gone to the south of France for a long holiday if she had not already spent all her money.
4. Which of the following is an example of the second conditional?- A I can't give you a lift to the shops, because I don't have a car.
- B If I had a car, I would give you a lift to the shops.
- C I will give you a lift to the shops if you don't mind waiting for ten minutes.
- D If my car hadn't broken down, I would have given you a lift to the shops.
- E My friend asked me to give her a lift to the shops, but my car had broken down.
5. Which of the following is an example of the third conditional?- A The TV will work if you plug it in first.
- B If we had a more modern TV set, we would have a lot more channels to choose from.
- C I would have watched my favourite TV program last night if we had not had a power cut.
- D I will watch my favourite TV program tonight if I can finish my work in time.
- E I can't watch my favourite TV program tonight because it has been replaced with a football match.
6. If it's warm and sunny tomorrow, we _____________ swim in the sea. (1st conditional)- A could
- B may
- C might
- D will
- E would
7. If you didn't eat so much late at night, you __________ sleep better. (2nd conditional)- A can
- B may
- might
- C should
- D will
- E would
8. If he had worked harder at school, he __________ got a place at university. (3rd conditional)- A can have
- B may have
- C might have
- D should have
- E will have
- F would have
9. The zero conditional is used for:- A unlikely or impossible things
- B real or possible situations
- C things that are true in general
- D things that are not true at all
- E something that didn't happen in the past, and it's too late now
10. The second conditional is used for:- A unlikely or impossible things
- B real or possible situations
- C things that are true in general
- D things that are not true at all
- E something that didn't happen in the past, and it's too late now
- A one
- B two
- C three
- D four
- A If I went out in rainy weather without an umbrella, I would get wet.
- B I will take my umbrella with me today, because it might rain.
- C If you remembered to take your umbrella with you, you wouldn't get wet.
- D If she had taken her umbrella with her, she wouldn't have got wet.
- E If you go out in rainy weather without an umbrella, you get wet.
- A Where would you like to go on holiday if you had plenty of money?
- B If I have enough money, I will go to the south of France for a long holiday.
- C The south of France is an expensive place to go for a holiday.
- D If I had enough money, I would go to the south of France for a long holiday.
- E She would have gone to the south of France for a long holiday if she had not already spent all her money.
- A I can't give you a lift to the shops, because I don't have a car.
- B If I had a car, I would give you a lift to the shops.
- C I will give you a lift to the shops if you don't mind waiting for ten minutes.
- D If my car hadn't broken down, I would have given you a lift to the shops.
- E My friend asked me to give her a lift to the shops, but my car had broken down.
- A The TV will work if you plug it in first.
- B If we had a more modern TV set, we would have a lot more channels to choose from.
- C I would have watched my favourite TV program last night if we had not had a power cut.
- D I will watch my favourite TV program tonight if I can finish my work in time.
- E I can't watch my favourite TV program tonight because it has been replaced with a football match.
- A could
- B may
- C might
- D will
- E would
- A can
- B may
- might
- C should
- D will
- E would
- A can have
- B may have
- C might have
- D should have
- E will have
- F would have
- A unlikely or impossible things
- B real or possible situations
- C things that are true in general
- D things that are not true at all
- E something that didn't happen in the past, and it's too late now
- A unlikely or impossible things
- B real or possible situations
- C things that are true in general
- D things that are not true at all
- E something that didn't happen in the past, and it's too late now
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 21.09.2021
Test your understanding of this English lesson
Test your understanding of the English lesson by answering these questions.
1. "When life gives
you lemons, make lemonade."
What does this saying mean?
·
А Bad things
never happen to anyone.
·
B When something
bad happens, people should try to turn it into something good.
·
C When something bad happens, people will always be unhappy.
2. When one door closes, another door __________.
·
A opens
·
B shuts
·
C breaks
3. Better __________ than never.
·
A fate
·
B rate
·
C late
4. What does it mean when someone says there's light at the end of the
tunnel?
·
A There's nothing.
·
B There's hope.
·
C There's daytime.
5. "Where there's a
will, there's a way."
What does the word "will" mean here?
·
A past and future
·
B black and white
·
C desire and motivation
6. Your friend has been trying to get a job for the past month, without
success. She's feeling quite depressed. What could you say to encourage her to
keep trying?
·
A Keep your head up!
·
B Keep your eyes up!
·
C Keep your chin
up!
7. The dinner party started at 7:00 pm. Your friend arrives at 8:30 pm. What do you say when he begins to apologize?
·
A It's okay. When life gives you lemons, make lemonade.
·
B It's okay.
Better late than never.
·
C It's okay, There's light at the end of the tunnel.
8. What does it mean to be optimistic?
·
A to be good-looking
·
B to be lucky
·
C to expect good
things to happen
9. People who see the glass as half-full are usually more __________.
·
A positive
·
B negative
·
C both
Choose one the following statements and comment on it.
Some people think that "Where there's a will, there's a way."/
What is your opinion? Do you agree with this statement?
Write 200–250 words.
Use the following plan:
− make an introduction (state the problem)
− express your personal opinion and give 2–3 reasons for your opinion
− express an opposing opinion and give 1–2 reasons for this opposing opinion
− explain why you don’t agree with the opposing opinion
− make a conclusion restating your position
Some people think that "Better late than never."
What is your opinion? Do you agree with this statement?
Write 200–250 words.
Use the following plan:
− make an introduction (state the problem)
− express your personal opinion and give 2–3 reasons for your opinion
− express an opposing opinion and give 1–2 reasons for this opposing opinion
− explain why you don’t agree with the opposing opinion
− make a conclusion restating your position
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 17.09.2021
Прочитайте приведённые ниже тексты. Преобразуйте, если необходимо, слова, напечатанные заглавными буквами в конце строк
As old as a brontosaurus
As old as a brontosaurus |
Прочитайте приведённый ниже текст. Преобразуйте, если необходимо, слова, напечатанные заглавными буквами в конце строк,
Why do we sleep?
Why do we sleep? |
SB p 14 ex C,D
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 25.02.2021
Task 4. Study the two photographs. In 1.5 minutes be ready to compare and contrast the photographs:
· give a brief description of the photos (action, location)
· say what the pictures have in common
· say in what way the pictures are different
· say which type of shopping you prefer
· explain why
You will speak for not more than 2 minutes (1215 sentences). You have to talk continuously.
Photo 1.
Photo 2.
Photo 1.
Photo 2.
№2
Add an indefinite pronoun to complete each sentence.
1. He put his glass of water down on the table, and _______________________ takes it!
2. The concert wasn`t so great! _________________________ was upset.
3. Does ___________________ have change so I can buy a book?
4. I wasn`t disappointed because _____________ who I invited came to the party.
5. ___________________ left the door opened, but _______ had come in.
6. He was surprised that _________________ sent him a birthday card in the mail, but did not sign the card.
7. That painting is so simple. _____________________ could have painted it.
8. ____________ told him the truth, but he didn`t believe.
9. She coudn`t find her notebook _________________ .
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 14.01.2021
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 10.12.2020
Join the sentences using WHO, WHEN, WHERE, WHICH or WHOSE:
1. She’s the girl. She works in the library. …………………………………………………………………………………
2. Corfu is an island. It has many beautiful beaches. …………………………………………………………………………………
3. Here’s the alarm clock. I bought it yesterday. …………………………………………………………………………………
4. I’ve spoken to John. His house was burgled last Monday. …………………………………………………………………………………
5. That’s the lady. Her jewellery was stolen. …………………………………………………………………………………
6. That is the radio. I won it in the competition. …………………………………………………………………………………
7. John is the man. His house was destroyed by the fire. …………………………………………………………………………………
8. There is the hospital. I was born there. …………………………………………………………………………………
9. That was the summer. I met my wife then. …………………………………………………………………………………
10. That is Fiona Webb. She is a famous dancer. …………………………………………………………………………………
11. France is the country. The best wine is produced there. …………………………………………………………………………………
12. 1945 was the year. The Second World War ended then. …………………………………………………………………………………
13. That’s the hotel. I stayed there last summer. ………………………………………………
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 10.11.2020
You have 40 minutes to do this task.
Comment on the following statement.
Some people think that you can have only one true friend.
What is your opinion? Do you agree with this statement?
Write 200 – 250 words.
Use the following plan:
− make an introduction (state the problem)
− express your personal opinion and give 2–3 reasons for your opinion
− express an opposing opinion and give 1–2 reasons for this opposing opinion
− explain why you don’t agree with the opposing opinion
− make a conclusion restating your position
10 th form 22.10.2020
!!! Send the answers on my email el.romanova2020@mail.ru
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 20.10.2020
You have received a letter from your English-speaking pen-friend Tom who writes:
…Last week our family went to the famous Niagara Falls. It was my first visit there and it was fun! We enjoyed the weather and the splashes of falling water on our faces. It reminded us of our last rafting trip. Where can you see beautiful water sights in Russia, if at all? Have you ever gone rafting? What do you think about extreme sports in general? By the way, we are going to Greece this summer… |
Write a letter to Tom.
In your letter
– answer his questions
– ask 3 questions about his trip to Greece
Write 100–140 words.
Remember the rules of letter writing.
လလလလလလလ
10 th form 05.10.2020
You have 20 minutes to do this task.
You have received a letter from your English-speaking pen-friend Tom who writes:
Last summer my parents and I went hiking to the mountains. We spent the whole week together and enjoyed it very much. How often do you take active holidays? Who do you think is the best company for you? What extreme sports would you like to try, if any, and why?
Last month our English class got an interesting project. We wrote a paper about interesting events in the past of our country …
Write a letter to Tom.
In your letter
- answer his questions
- ask 3 questions about his project paper
Write 100 140 words.
Remember the rules of letter writing.
လလလလလလလ
A report
Reported speech (commands and requests)
№. 2 Change into direct speech
|
Reported questions

direct speech: 'Do you work from home?' he said.
indirect speech: He asked me if I worked from home.
direct speech: 'Who did you see?' she asked.
indirect speech: She asked me who I'd seen.
direct speech: 'Could you write that down for me?' she asked.
indirect speech: She asked me to write it down.
Grammar explanation
direct speech: 'Do you like working in sales?' he asked.
indirect speech: He asked me if I liked working in sales.
Yes/no questions
'Are you going to the Helsinki conference?'
'Have you finished the project yet?'
- He asked me if I was going to the Helsinki conference.
- She asked us whether we'd finished the project yet.
Questions with a question word
'What time does the train leave?'
'Where did he go?'
- He asked me what time the train left.
- She asked where he went.
Reporting verbs
'Did you bring your passports?'
'When could you get this done by?'
- She wanted to know if they'd brought their passports.
- He wondered when we could get it done by.
Offers, requests and suggestions
'Would you like me to help you?'
'Can you hold this for me, please?'
- He offered to help me.
'Why don't we check with Joel?'
- She asked me to hold it.
- She suggested checking with Joel.
1 What is the main problem of our Planet right now?
2 What have we do to save the Panet?
3 What can you do for the enviroment now?
























Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий